git
Git 是一个开源的分布式版本控制系统(Distributed Version Control System,DVCS),用于敏捷高效地处理任何或小或大的项目
Git 的下载 : ==> git-scm-downloads
Installing Git ==> Installing-Git
三种状态
git 有三种状态
已提交(committed)表示数据已经安全的保存在本地数据库中已修改(modified)表示修改了文件,但还没保存到数据库中已暂存(staged)表示对一个已修改文件的当前版本做了标记,使之包含在下次提交的快照中
git 项目的三个工作区域
git 仓库 .git directory(Repository)是 Git 用来保存项目的元数据和对象数据库的地方, clone 的时候就是 copy 这里的数据.工作目录 Working Directory是对项目某个版本独立提取(pull)出来的内容暂存区域 Staging Area是一个文件,保存了下次将提交的文件列表信息,一般在 git 仓库目录中.
基本的 Git 工作流程
- 在工作目录中修改文件
- 暂存文件,将文件的快照放入暂存区域
- 提交更新,找到暂存区域的文件,将快照(snapshot)永久性存储到 Git 仓库目录中
命令行
- Mac ==> 终端(Terminal)
- Windows ==> 命令窗口(Command Prompt) or PowerShell
初次运行 git 前的配置
用户信息
当安装完 Git 应该做的第一件事就是设置用户名和邮件地址.每次 git 提交都会使用这些信息.
1 | $ git config --global user.name "Your Name" |
git config中如果使用了--global,本机的所有 git 仓库都会使用该配置.
检查配置信息
git config --list列出所有 Git 当前配置git config <key>检查 Git 的某一项配置 如git conifg user.name
获取帮助
git 手册随 git 一起安装在本地, 全英文 … English English English
1 | $ git help <verb> |
1.Getting a Git Repository
有两种获取 Git 项目仓库(Git Repository)的方法:
- You can take a local directory that is currently not under version control, and turn it into a Git repository, or
- You can clone an existing Git repository from elsewhere.
1.1 Initializing a Repository in an Existing Directory
If you have a project directory that is currently not under version control and you want to start controlling it with Git, you first need to go to that project’s directory.
- cd 到现有项目目录下
cd MyProject git init该命令创建一个名为.git的子目录
git init : This creates a new subdirectory named .git that contains all of your necessary repository files — a Git repository skeleton. At this point, nothing in your project is tracked yet.
在这个时候,我们仅仅是做了一个初始化的操作,项目里的文件还没有被跟踪
如果我们想要对 existing files 做 version-controlling, we should probably begin tracking those files and do an initial commit
1 | $ git add *.c |
1.2 Cloning an Existing Repository
If you want to get a copy of an existing Git repository — for example, a project you’d like to contribute to — the command you need is git clone.
当执行git clone命令的时候,默认配置下远程 Git 仓库中的每一个文件的每一个版本都将被拉取(pull)下来
clone repository 的命令是git clone [url], 比如, 要克隆 libgit2
1 | $ git clone https://github.com/libgit2/libgit2 |
会在当前目录下创建一个名为libgit2的目录,从远程仓库拉取下所有数据放入这个目录中,并在这个目录下初始化一个.git文件夹
- 在 clone 远程仓库时,自定义本地仓库名字
1 | $ git clone https://github.com/libgit2/libgit2 mylibgit |
ps.在 Windows 中使用 Linux 命令 ==> git bash , git bash 中 Vim 退回
:q
2. Recording Changes to the Repository
Remember that each file in your working directory can be in one of two states: tracked or untracked. Tracked files are files that were in the last snapshot; they can be unmodified, modified, or staged. In short, tracked files are files that Git knows about.
Untracked files are everything else — any files in your working directory that were not in your last snapshot and are not in your staging area. When you first clone a repository, all of your files will be tracked and unmodified because Git just checked them out and you haven’t edited anything.
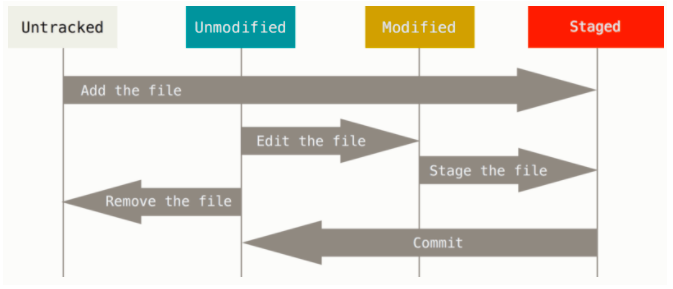
- The lifecycle of the status of your files
2.1 Checking the Status of Files
The main tool you use to determine which files are in which state is the git status command
1 | $ git status |
This means you have a clean working directory — in other words, none of your tracked files are modified.
if we add a new file to our project, a simple README.md file. If the file didn’t exist before, and we run git status
1 | $ git status |
Untracked files:新建的文件出现在Untracked files下面,未跟踪都文件意味着 Git 在之前都快照(提交)中没有这些文件,
git 不会自动将新建文件纳入跟踪范围, 我们使用git add <file>来跟踪某个文件
2.2 Tracking New Files
To begin tracking the README file, you can run this:
1 | $ git add README |
run git status command again
1 | $ git status |
Changes to be committed: 在这行下面都文件表示是已暂存状态.如果现在提交,name 该文件此时此刻的版本将被保留在历史记录中.
2.3 Staging Modified Files
如果我们修改一个已被跟踪都文件CONTRIBUTING.md.然后运行git status
1 | $ git status |
Changes not staged for commit: 表示已跟踪文件内容发生了变化,还没有放到暂存区.要暂存这次更新,需要运行git add
git add: 1. 可以用它开始跟踪新文件 2. 把已跟踪都文件放到暂存区 3.用于合并时把有冲突的文件标记为已解决状态等; 注意:add 成功后是不给提示的,会换行进入下一个输入- 可以理解
git add为将该内容添加到下一次提交中而不是将一个文件添加到项目中 add precisely this content to the next commitrather thanadd this file to the project
运行git add CONTRIBUTING.md将”CONTRIBUTING.md”放到暂存区,在看看git status输出
1 | $ git status |
现在两个文件都已暂存,下次提交就会一并记录到仓库. 假设这时我们在CONTRIBUTING.md里再加条注释保存后,再运行git status
1 | $ git status |
这时CONTRIBUTING.md同时出现在暂存区和非暂存区,因为 git 只暂存了运行git add命令时都版本,如果现在提交,CONTRIBUTING.md的版本是最后一次运行 git add 命令时的那个版本,而不是运行 git commit 时,在工作目录中的当前版本.所以,**运行了 git add 之后又作了修订的文件,需要重新运行 git add 把最新版本重新暂存起来**
2.4 Short Status
当我们使用git status -s或git status --short,将得到一种更简洁的格式输出
1 | $ git status -s |
2.5 Viewing Your Staged and Unstaged Changes
查看已暂存和未暂存的修改,显示具体那些行发生了变化,可以用git diff命令
当要查看尚未暂存的文件更新了哪些部分,不加参数直接输入
git diff- 该命令比较的是工作目录中当前文件和暂存区域快照之前的差异,也就是修改之后还没有暂存起来的变化差异
要查看已暂存的将要添加到下次提交里的内容,可以用
git diff --cached版本 1.6.1 或以上还可以用git diff --staged
ps.
git diff本身只显示尚未暂存的改动,而不是自上次提交以来所做的所有改动。 所以有时候一下子暂存了所有更新过的文件后,运行 git diff 后却什么也没有,就是这个原因
2.6 Committing Your Changes
当暂存区已经准备妥当就可以提交了,在提交前,一定要确认还有什么修改过的或新建的文件还没有git add过,否则提交的时候不会记录这些还没有暂存起来的变化.
- 每次提交前,先
git status查看下, 是不是所有修改的放入暂存区(git add),然后再运行提交命令git commit -m "commit message"
1 | $ git commit -m "git 提交测试" |
You can see that the commit has given you some output about itself: 1. which branch you committed to (master), 2. what SHA-1 checksum(SHA-1哈希校验和) the commit has (463dc4f), 3. how many files were changed, 4. and statistics about lines added and removed in the commit.
每次git commit -m '<msg>'提交时记录的是放在暂存区的快照. 每次运行提交操作,都是对项目作一次快照,以后可以回到这个状态
2.7 Skipping the Staging Area
跳过使用暂存区: 在提交的时候,使用git commit -a -m '<msg>',git 就会自动把所有已经跟踪过渡文件暂存起来一并提交,从而跳过git add步骤
2.8 Removing Files
To remove a file from Git, you have to remove it from your tracked files (more accurately, remove it from your staging area) and then commit.要从 git 中移除某个文件,就必须从暂存区中移除,然后提交
当我们在工作目录中手工删除某个文件,运行git status时就会在”Changes not staged for commit:”中看到deleted:,
然后再运行git rm记录此次移除文件的操作. 下次提交时,该文件就不再纳入版本管理了
如果删除之前修改过并且已经放到暂存区(git add),则必须要用强制删除选项 -f(force)
3.0 Viewing the Commit History
查看历史提交
git log
1 | $ git log |
默认不用任何参数时,git log会按提交时间列出所有的更新,它会列出每个提交的SHA-1校验和 Author email date and commit message
-p用来显示每次提交的内容差异,同时可以加上-2仅显示最近两次的提交
1 | $ git log -p -2 |
--stat 显示每次提交的统计信息
1 | $ git log --stat |
--pretty 指定使用不用于默认格式的方式展示 有oneline short full fuller --pretty=format:"%h - %an"等
1 | $ git log --pretty=oneline |
Undoing Things
当我们在一次提交git commit -m <msg>完后发现提交信息写错了,或者有漏掉文件没有git add,可以运行撤销操作:
1 | $ git commit --amend |
当我们运行上面命令时,会出现 vim 编辑窗口,刚进入编辑器的时候,是 vim 的 normal 模式,按键盘i a o都可以进入 Vim 的 insert 模式进行编辑(编辑必须在 insert 模式中进行)
git 中 vim 的常用几个命令,按 Esc 退出插入模式后,输入:,
:w保存编辑后文件内容,不退出 vim 编辑器:wq保存并退出 vim:q退出 vimps.terminal 中切换到 d 盘
cd /dorcd d:,MinGW(Minimalist GNUfor Windows)- vsCode 中使用 git bash, VScode 首选项 User Settings 中设置
1 | "terminal.integrated.shell.windows": "C:\\Program Files\\Git\\bin\\bash.exe" |
执行git commit --amend,在 vim 中编辑完 message 后,:wq退出,我们git status查看,会发现只有一次提交记录,上一次的会被 overwrite 重写
1 | $ git commit -m 'initial commit' |
You end up with a single commit — the second commit replaces the results of the first.
Unstaging a Staged File
当我们运行git add .orgit add *暂存了两个(所有的)修改文件,但是我们原本想要将它们作为两次独立的修改提交,
那么取消暂存中的一个使用git reset HEAD '<file>'来取消暂存的某个文件
Unmodifying a Modified File
1 | Changes not staged for commit: |
如果我们不想保留对某个文件的修改(文件未放入暂存区才可以使用),想要将它还原成上次提交时的样子(或者刚把它放入工作区的样子)
git checkout --'<filename>'注意加上文件后缀名.md or .js等
执行完后,我们可以看见后来做出的修改被原来提交的版本替换了,注意:我们在git commit后所做的所有修改的都会消失
如果我们仍向保留对那个文件做出的修改,但现在又需要撤销,我们可以新建一个branch分支来保存进度.
Git 回滚到某个 commit
注意使用–hard 不可逆
1 | $ git reset --hard HEAD^ 回退到上个版本 |
ps.
git commit -a -m===git commit -am